The Untapped Potential of Geothermal Energy in the UK
Geothermal Energy: A Renewable Resource for the Future
Geothermal energy, the heat stored within the earth’s crust and mantle, is a renewable and sustainable energy source that has the potential to play a significant role in the United Kingdom’s transition towards a low-carbon future. While the UK’s geothermal energy resources have long been underutilized, recent developments and growing interest in this technology have brought it to the forefront of the country’s renewable energy landscape.
The UK’s Geothermal Energy Landscape

According to the latest data from the International Geothermal Association (IGA), the UK’s installed geothermal power capacity stood at just 12 megawatts (MW) as of 2020, lagging behind countries such as Iceland, the United States, and Italy, which have much more extensive geothermal energy sectors. However, the UK’s geothermal potential is believed to be substantial, particularly in areas with favorable geological conditions, such as the Southwest and parts of Scotland.
Geothermal Energy Sources and Technologies
The UK’s geothermal energy resources can be broadly categorized into two main types: shallow geothermal systems and deep geothermal systems. Shallow geothermal systems, which utilize the relatively stable temperatures found a few meters below the Earth’s surface, are primarily used for heating and cooling applications, while deep geothermal systems, which tap into the higher-temperature resources found at greater depths, have the potential to generate electricity.
Harnessing the UK’s Geothermal Potential

The UK government and the geothermal industry have recognized the significant untapped potential of geothermal energy and have taken steps to promote its development and utilization across the country.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
The UK’s policy and regulatory landscape for geothermal energy has been evolving in recent years, with the aim of providing a supportive environment for the deployment of geothermal projects. Key initiatives include:
The Climate Change Act
The UK’s Climate Change Act of 2008 has been a driving force behind the country’s renewable energy transition, setting a legally binding target to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. This has created a strong impetus for the development of geothermal energy as a low-carbon alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources.
The Renewable Energy Directive

The European Union’s Renewable Energy Directive, which sets a target of at least 32% of the EU’s energy consumption to come from renewable sources by 2030, has also influenced the UK’s geothermal energy policies and regulations.
Support Schemes and Incentives
To encourage the deployment of geothermal energy projects, the UK government has implemented various support schemes and incentives, such as the Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI) and the Contracts for Difference (CfD) scheme, which have provided financial support for both shallow and deep geothermal technologies.
Geothermal Resource Assessments and Exploration
A critical component of unlocking the UK’s geothermal potential is the ongoing assessment and exploration of the country’s geothermal resources. Several initiatives, such as the UK Geoenergy Observatories project, have been undertaken to improve the understanding of the UK’s geothermal geology and to identify the most promising areas for development.
Geothermal Energy Applications in the UK

The UK’s geothermal energy sector is poised to offer a diverse range of applications, from heating and cooling to electricity generation, each with its unique benefits and challenges.
Shallow Geothermal Systems
Shallow geothermal systems, which utilize the stable temperatures found a few meters below the Earth’s surface, are primarily used for heating and cooling applications in buildings and homes. These systems, often referred to as ground-source heat pumps, have gained traction in the UK, thanks to their energy efficiency and low-carbon footprint.
Deep Geothermal Systems
Deep geothermal systems, which tap into the higher-temperature resources found at greater depths, have the potential to generate electricity. While the UK’s deep geothermal resources are less well-understood than its shallow resources, several pilot projects and feasibility studies have been undertaken to explore the possibility of geothermal power generation.
Direct Use Applications
In addition to heating, cooling, and electricity generation, geothermal energy can also be used for direct use applications, such as industrial processes, district heating, and agricultural applications. These direct use applications can help to further diversify the UK’s geothermal energy portfolio and maximize the utilization of the country’s geothermal resources.
Challenges and Opportunities
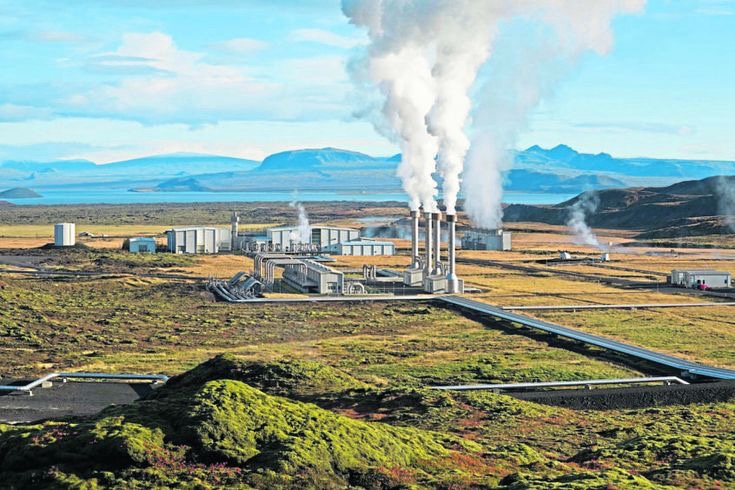

As the UK seeks to harness the potential of geothermal energy, it faces a range of challenges and opportunities that will shape the future of this renewable energy sector.
Technical Challenges
One of the primary challenges facing the UK’s geothermal energy sector is the technical complexity and high upfront costs associated with deep geothermal projects. Drilling deep wells and accessing high-temperature resources require specialized expertise and equipment, which can be a significant barrier to widespread deployment.
Regulatory and Policy Barriers
The UK’s regulatory and policy landscape for geothermal energy has been evolving, but there are still some barriers that need to be addressed. For example, the permitting process for geothermal projects can be time-consuming and complex, and the lack of a clear legislative and regulatory framework for deep geothermal development has been a concern for the industry.
Opportunities for Innovation and Collaboration
Despite the challenges, the UK’s geothermal energy sector presents significant opportunities for innovation and collaboration. The country’s strong research and development capabilities, particularly in the fields of geology, engineering, and materials science, can help drive technological advancements and cost reductions in geothermal energy technologies.
Synergies with other Renewable Energy Sources
Geothermal energy can be integrated with other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to create hybrid energy systems that enhance the overall reliability and flexibility of the UK’s energy network. Leveraging these synergies can help to maximize the benefits of geothermal energy and accelerate the country’s transition towards a low-carbon future.
Conclusion
The United Kingdom’s geothermal energy sector holds immense untapped potential, offering a versatile and sustainable energy solution that can play a crucial role in the country’s renewable energy transition. While the UK’s geothermal energy landscape has lagged behind other nations in the past, recent developments and growing interest in this technology have created a renewed sense of optimism and momentum.
By addressing the technical, regulatory, and policy challenges, and harnessing the opportunities for innovation and collaboration, the UK can unlock the full potential of its geothermal resources. This will not only contribute to the country’s decarbonization efforts but also create new economic opportunities and foster the development of a thriving geothermal energy industry.
As the UK continues to push forward with its renewable energy agenda, the development of geothermal energy should be at the forefront of its priorities, as it represents a reliable, low-carbon, and largely untapped resource that can help the country achieve its ambitious climate goals and secure a sustainable energy future.
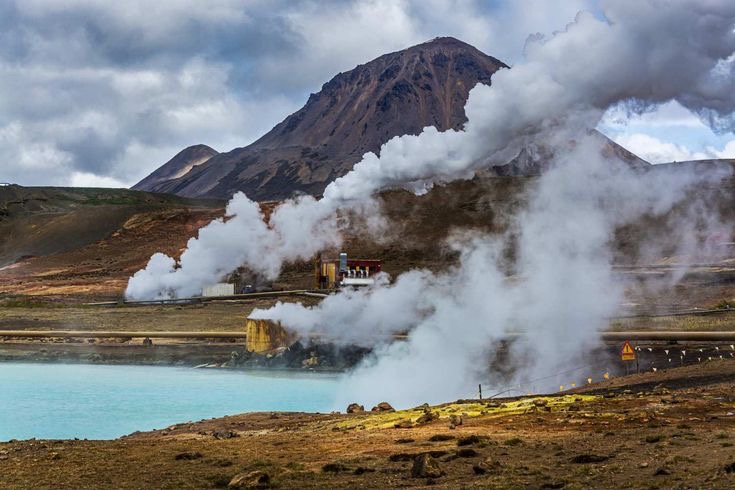



[…] geothermal energy is a key player, it cannot be implemented everywhere, making nuclear energy an attractive […]