The Potential of Marine Energy in Spain
Marine energy, derived from oceanic forces such as tides, waves, and currents, represents a significant opportunity for Spain to diversify its energy portfolio and enhance its commitment to renewable energy. With its extensive coastline and favorable geographic conditions, Spain is well-positioned to harness marine energy as a sustainable resource. This article delves into the current state of marine energy in Spain, its potential, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding Marine Energy
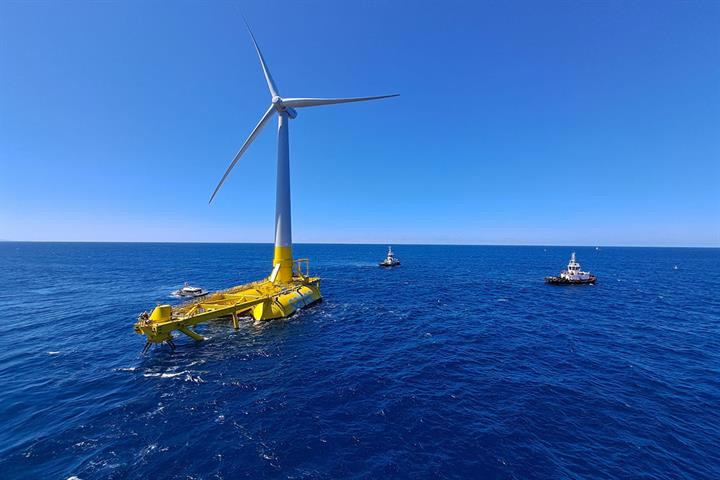

What is Marine Energy?
Marine energy encompasses various technologies that convert the energy produced by oceanic phenomena into electricity or other forms of usable energy. The primary types of marine energy include:
- Tidal Energy: Generated from the gravitational pull of the moon and sun, leading to the movement of water in and out of estuaries and coastal areas.
- Wave Energy: Derived from the surface movement of the sea, generated by wind and atmospheric conditions.
- Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC): Exploits temperature differences between warmer surface water and colder deep water to generate electricity.
The Importance of Marine Energy
Marine energy plays a critical role in the transition to a sustainable energy future. It offers several advantages:
- Renewable Source: Marine energy is abundant and continuously replenished by natural processes.
- Predictability: Unlike solar and wind energy, marine energy sources, particularly tidal energy, are highly predictable and can be forecasted with accuracy.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Utilizing marine energy contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global climate goals.
The Marine Energy Landscape in Spain
Current Status of Marine Energy in Spain
Spain has made notable strides in the field of marine energy, although it remains in the early stages of development compared to other renewable sectors. According to the Spanish Marine Energy Association (APPA), as of 2022, Spain has an installed capacity of approximately 10 MW from marine energy technologies, primarily focused on wave energy projects.
Key Statistics
- Total Installed Marine Energy Capacity: 10 MW
- Projects in Development: 15 projects with a combined capacity of over 100 MW expected by 2025.
- Investment in Marine Energy (2022): Approximately €50 million.
Geographical Advantages
Spain boasts a long coastline of over 7,900 kilometers, making it one of the largest in Europe. The geographic diversity includes:
- Atlantic Coast: Particularly favorable for tidal energy.
- Mediterranean Sea: Offers potential for wave energy projects.
- Canary Islands: Unique opportunities for OTEC due to significant temperature differentials.
Applications of Marine Energy in Spain
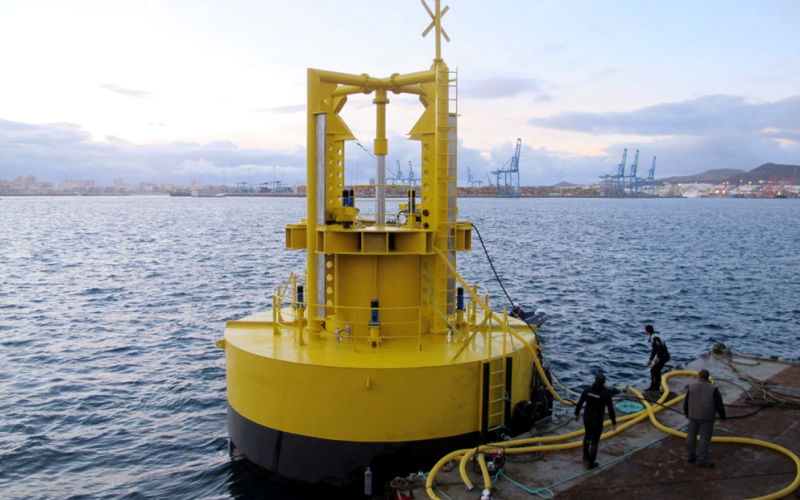

Wave Energy
Spain is home to several wave energy projects, with notable advancements in regions such as Galicia and the Basque Country. The Mutriku Wave Energy Converter, operational since 2011, is one of the first commercial wave energy plants in Spain, with a capacity of 300 kW.
Key Projects
- Mutriku Wave Energy Converter:
- Capacity: 300 kW
- Location: Basque Country
- Status: Operational
Tidal Energy
Tidal energy has seen limited deployment in Spain, but several pilot projects are underway. The Tidal Energy Project in the Bay of Biscay aims to harness the robust tidal currents in the region.
Key Projects
- Bay of Biscay Tidal Project:
- Capacity: 1 MW (pilot phase)
- Status: Under development
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC)

The Canary Islands are exploring OTEC due to the significant temperature gradients found in the region. This technology has the potential to provide a continuous energy supply, leveraging the thermal differences in ocean water.
Government Policies and Initiatives
National Energy and Climate Plan (NECP)
Spain’s National Energy and Climate Plan (NECP) outlines the government’s commitment to increasing the share of renewable energy, including marine energy, in its energy mix. The plan aims for a 74% share of renewable energy in electricity generation by 2030, with specific targets for marine energy development.
EU Support and Funding
Spain benefits from EU initiatives that support the development of marine energy technologies. The Horizon Europe program allocates funds for research and innovation in renewable energy, including marine technologies.
Regulatory Framework
Spain is working to streamline the regulatory process for marine energy projects. The Ministry for the Ecological Transition is focused on creating a favorable environment for investment and innovation in the marine energy sector.
Challenges Facing Marine Energy in Spain

Technological Hurdles
The marine energy sector faces several technological challenges, including:
- Efficiency and Reliability: Many marine energy technologies are still in the testing phase, and efficiency improvements are necessary for commercial viability.
- Environmental Impact: Assessing and mitigating the environmental impact of marine energy installations is crucial for gaining public and regulatory acceptance.
Financial Barriers
While investments in marine energy are increasing, the sector still relies heavily on public funding and incentives. Securing private investment remains a challenge due to perceived risks and uncertain returns.
Public Awareness and Acceptance
Public awareness of marine energy is limited. Educating communities about the benefits of marine energy and addressing concerns about environmental impacts can help increase acceptance.
Economic Impact of Marine Energy
Job Creation
The marine energy sector has the potential to create thousands of jobs across various fields, including engineering, construction, and maintenance. According to the Spanish Marine Energy Association, the sector could generate approximately 5,000 jobs by 2030.
Investment Opportunities
The growing interest in marine energy presents significant investment opportunities. The estimated investment required to develop marine energy capacity to 500 MW by 2030 is around €2 billion.
Future Prospects for Marine Energy in Spain
Technological Innovations
Research and development will be critical to overcoming current challenges in the marine energy sector. Innovations in turbine design, energy storage, and materials science can enhance the efficiency and durability of marine energy systems.
Expansion of Marine Energy Projects

Spain is witnessing a growing number of marine energy projects. The government’s commitment to renewable energy, combined with advancements in technology, is expected to drive growth in the sector. Collaborative efforts between government, academia, and industry will be essential for success.
Community Engagement and Initiatives
Engaging local communities in marine energy projects can foster support and facilitate development. Community-based initiatives that highlight the benefits of marine energy, such as job creation and energy independence, can enhance public acceptance.
Conclusion
Marine energy in Spain holds tremendous potential for contributing to the country’s renewable energy goals. With a favorable geographic position, supportive government policies, and growing public interest, Spain is poised to harness this abundant resource. While challenges remain, the future of marine energy in Spain looks promising, paving the way for a sustainable energy landscape.



