The Promising Future of Marine Energy in Portugal
Marine energy, derived from oceanic sources such as tides, waves, and currents, is gaining traction as a significant component of Portugal’s renewable energy strategy. With an extensive coastline and favorable geographical conditions, Portugal is well-positioned to harness marine energy to meet its growing energy needs. This article explores the current state of marine energy in Portugal, its potential, challenges, and future prospects, supported by official statistics and sources.

Understanding Marine Energy
What is Marine Energy?
Marine energy refers to the energy obtained from oceanic sources, including:
- Wave Energy: Energy generated from the surface motion of ocean waves.
- Tidal Energy: Energy produced from the rise and fall of tides.
- Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC): Energy derived from the temperature differences between warmer surface water and colder deep water.
Importance of Marine Energy in Portugal
Marine energy is an essential part of Portugal’s renewable energy mix. As of 2022, marine energy accounts for approximately 0.5% of the country’s total electricity generation. While this may seem minimal, the potential for expansion is significant, particularly given Portugal’s 3,000 kilometers of coastline.
Current Marine Energy Capacity in Portugal
Installed Marine Energy Capacity

As of 2022, Portugal has an installed marine energy capacity of approximately 20 MW. This capacity primarily comes from pilot projects and experimental facilities focused on wave and tidal energy.
Key Statistics
- Total Installed Marine Energy Capacity: 20 MW
- Annual Marine Energy Generation (2022): Approximately 0.1 TWh
- Percentage of Total Electricity Generation: 0.5%
Major Marine Energy Projects in Portugal
Portugal is home to several notable marine energy projects:
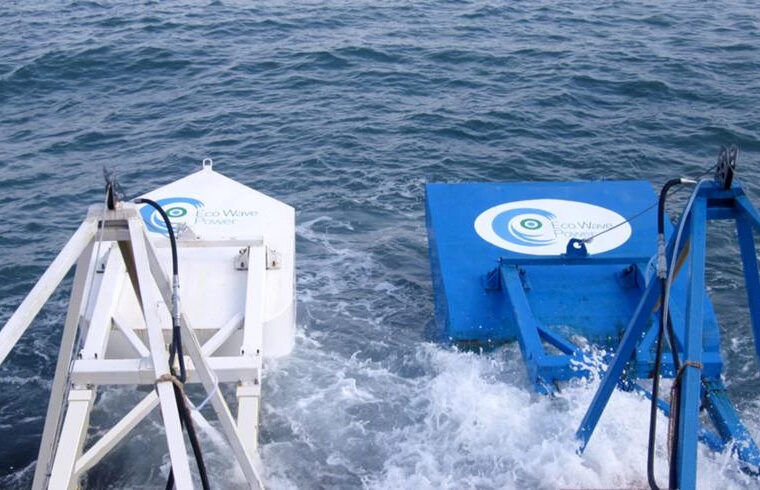
- Pelamis Wave Energy Converter: This pioneering project, located off the coast of Aguçadoura, was one of the first commercial wave energy farms in the world, with a capacity of 2.25 MW.
- WaveRoller Project: Situated near Peniche, this project aims to harness wave energy using submerged devices to convert wave motion into electricity.
- Tidal Energy Project in the Ria Formosa: This pilot project explores the feasibility of tidal energy generation using underwater turbines.
The Role of Marine Energy in Portugal’s Renewable Energy Strategy
National Energy and Climate Plan (NECP)
Portugal’s National Energy and Climate Plan (NECP) outlines the country’s commitment to increasing the share of renewable energy sources. The plan aims for 80% of electricity generation to come from renewable sources by 2030, with marine energy expected to play a vital role in achieving this ambitious target.
EU Regulations and Support
As a member of the European Union, Portugal is subject to various regulations aimed at promoting renewable energy. The EU Renewable Energy Directive provides a framework for member states to enhance their renewable energy shares, including marine energy.
Advantages of Marine Energy
Renewable and Sustainable
Marine energy is a renewable resource that produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions. It provides a stable and reliable source of energy, contributing to energy security and sustainability.
Abundant Resources
With its extensive coastline and favorable ocean conditions, Portugal has access to significant marine energy resources. This abundance positions the country to harness energy from waves, tides, and currents effectively.
Job Creation and Economic Development
The development of marine energy projects can stimulate local economies by creating jobs in construction, maintenance, and operation. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the marine energy sector has the potential to create thousands of jobs in Portugal.
Challenges Facing Marine Energy in Portugal
Technological Barriers
Marine energy technology is still in its infancy, and many concepts are yet to be commercially viable. Continued investment in research and development is essential to overcome technological challenges and improve efficiency.
Environmental Concerns
Marine energy projects can have environmental impacts, such as disrupting marine ecosystems and affecting local wildlife. Comprehensive environmental assessments are crucial to mitigate these impacts.
High Initial Costs
The capital costs associated with marine energy projects are often higher than those for other renewable energy sources. Securing funding and investment can be a significant barrier to the development of marine energy facilities.
Future Prospects for Marine Energy in Portugal
Technological Innovations
Advancements in technology can enhance the efficiency and sustainability of marine energy production. Innovations such as improved wave energy converters and tidal turbines may increase energy yield and reduce costs.
Expansion of Pilot Projects
Portugal has the opportunity to expand its portfolio of pilot projects to test various marine energy technologies. By investing in pilot programs, the country can gain valuable insights into the feasibility and effectiveness of marine energy generation.
Integration with Other Renewable Sources
Integrating marine energy with other renewable sources, such as wind and solar, can enhance energy security and grid stability. This hybrid approach can help balance supply and demand, particularly during fluctuating weather conditions.
Conclusion
Marine energy is a promising component of Portugal’s renewable energy landscape, offering numerous benefits for energy security, sustainability, and economic development. With its existing capacity and potential for growth, marine energy can play a crucial role in achieving Portugal’s energy and climate goals. While challenges remain, technological innovations and supportive policies can help Portugal harness its marine energy potential for a sustainable future.
References
- National Energy and Climate Plan (NECP)
- International Energy Agency (IEA)
- European Commission – Renewable Energy
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
- Marine Energy Europe



