The Expanding Role of Bioenergy in Portugal
Bioenergy is increasingly becoming a pivotal part of Portugal’s renewable energy strategy. With a strong commitment to sustainability and reducing carbon emissions, Portugal is well-positioned to leverage its abundant biomass resources to enhance energy security and support rural development. This article explores the current state of bioenergy in Portugal, its potential, challenges, and future prospects, supported by key statistics and insights from official sources.
Understanding Bioenergy
What is Bioenergy?
Bioenergy refers to energy derived from organic materials, including plant and animal waste, that can be converted into heat, electricity, or biofuels. It encompasses several categories:
- Biomass: Organic materials used directly for energy production.
- Biofuels: Fuels produced from biomass, such as biodiesel and bioethanol.
- Biogas: Gaseous fuel produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic matter.
Importance of Bioenergy in Portugal
Bioenergy plays a critical role in Portugal’s energy landscape. It contributes to energy security, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and promotes rural development. As of 2022, bioenergy accounts for approximately 6.5% of Portugal’s total energy consumption, highlighting its growing importance in the renewable energy mix.
Current Bioenergy Capacity in Portugal
Installed Bioenergy Capacity
As of 2022, Portugal’s total installed bioenergy capacity is approximately 3,200 MW. This capacity is derived from various sources, including biomass power plants, biogas facilities, and biofuel production plants.
Key Statistics
- Total Installed Bioenergy Capacity: 3,200 MW
- Annual Bioenergy Generation (2022): Approximately 12 TWh
- Percentage of Total Electricity Generation: 6.5%
Major Bioenergy Facilities in Portugal
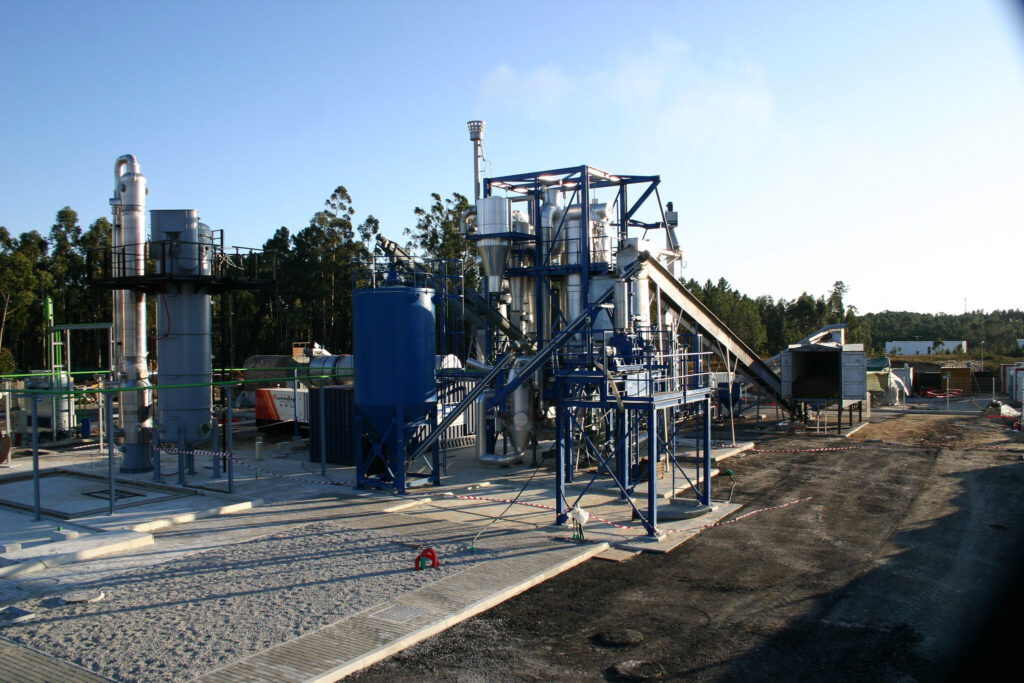

Portugal is home to several significant bioenergy facilities, including:
- Póvoa de Varzim Biomass Power Plant: Located in the northern region, with a capacity of 25 MW.
- Biogas Plant in Almeirim: This facility processes organic waste to produce biogas for electricity generation and heat.
- Biodiesel Plant in Sines: A key player in biofuel production, focusing on local agricultural residues.
The Role of Bioenergy in Portugal’s Renewable Energy Strategy
National Energy and Climate Plan (NECP)
Portugal’s National Energy and Climate Plan (NECP) outlines the country’s commitment to increasing the share of renewable energy sources, with bioenergy playing a vital role. The plan aims for 80% of electricity generation to come from renewable sources by 2030, with bioenergy contributing significantly to this target.
EU Regulations and Support

As a member of the European Union, Portugal adheres to various regulations aimed at promoting renewable energy. The EU Renewable Energy Directive sets ambitious targets for member states, including increasing the use of bioenergy.
Advantages of Bioenergy
Renewable and Sustainable
Bioenergy is a renewable resource that utilizes organic materials, which are replenishable through agricultural practices. This reduces dependence on fossil fuels and contributes to lower carbon emissions.
Waste Management Solutions
Bioenergy provides an effective solution for waste management. Organic waste from agriculture, forestry, and municipal sources can be converted into energy, reducing landfill use and associated emissions.
Rural Development and Job Creation
The bioenergy sector contributes to rural development by creating jobs in biomass production, processing, and energy generation. According to the Portuguese Bioenergy Association (APBIO), the sector could generate approximately 25,000 jobs by 2030.
Challenges Facing Bioenergy in Portugal

Competition for Resources
Bioenergy production often competes with food production for agricultural resources. This competition can lead to rising food prices and concerns about food security.
Technological and Infrastructure Barriers
The bioenergy sector faces challenges related to technology and infrastructure. Many bioenergy facilities require significant investment in advanced technologies and distribution networks.
Regulatory and Bureaucratic Hurdles
Navigating the regulatory landscape for bioenergy projects can be complex. Delays in obtaining permits and approvals can hinder the development of new projects.
Future Prospects for Bioenergy in Portugal
Technological Innovations
Advancements in technology can enhance the efficiency and sustainability of bioenergy production. Innovations such as improved anaerobic digestion processes and advanced biofuel production methods can increase yield and reduce costs.
Expansion of Biomass Resources

Portugal has significant potential to expand its biomass resources. Agricultural residues, forestry by-products, and organic waste from urban areas can be utilized to boost bioenergy production.
Integration with Other Renewable Sources
Integrating bioenergy with other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, can enhance energy security and grid stability. This hybrid approach can help balance supply and demand, particularly during fluctuating weather conditions.
Conclusion
Bioenergy is a vital component of Portugal’s renewable energy landscape, offering numerous benefits for energy security, waste management, and rural development. With its extensive capacity and potential for growth, bioenergy can play a crucial role in achieving Portugal’s energy and climate goals. While challenges remain, technological innovations and supportive policies can help Portugal harness its bioenergy potential for a sustainable future.
References
- National Energy and Climate Plan (NECP)
- Portuguese Bioenergy Association (APBIO)
- Ministry of Environment and Climate Action
- International Energy Agency (IEA)
- European Commission – Renewable Energy



